Content

If a company’s Times Interest Earned Ratio falls below 1, the company will have to fund its required interest payments with cash on hand or borrow more funds to cover the payments. Typically, a Times Interest Earned Ratio below 2.5 is considered a warning sign of financial distress. Calculating a company’s debt to equity ratio is straight forward, and the debt and equity components can be found on a company’s respective balance sheet. For more advanced analysis, financial analysts can calculate a company’s debt to equity ratio using market values if both the debt and equity are publicly traded. Interest payments on debt are tax deductible, while dividends on equity are not. Returns to purchasers of debt are limited to agreed- upon terms (i.e., interest rates), however, they have greater legal protection in the event of a bankruptcy.

The account was divided between internal and external legal services. Within each category were created more separate accounts for different specific legal expenditures. The change will allow governments to analyze and compare costs much more effectively. This also aligns accounting records with procedures auditors are required by professional standards to perform an audit on legal liabilities, so it will help make the audit process more efficient.
What Does Long Term Liabilities Mean?
Financial obligations of a company occurring due to previous events which are not due for more than one year in the future. As a business owner, you’ll probably incur some liabilities when running your business. Regardless what your business sells or does, you’ll need capital to perform its operations. You may already have some capital available, but in many instances, you’ll have to secure financing from an outside source, such as a bank or lender. long term liabilities examples There are both current and long-term liabilities, and it’s important that you familiarize yourself with these two primary types. Some advance refundings are intended to achieve short-term budgetary savings by extending debt service requirements further into the future. In these cases, total debt service requirements over the life of the new debt may be more or less than the total service requirements over the life of the existing debt.
P3 Health Partners : CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (UNAUDITED) FOR THE THREE AND NINE MONTHS ENDED SEPTEMBER 30, 2021 and 2020 – Form 8-K – marketscreener.com
P3 Health Partners : CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (UNAUDITED) FOR THE THREE AND NINE MONTHS ENDED SEPTEMBER 30, 2021 and 2020 – Form 8-K.
Posted: Thu, 09 Dec 2021 22:22:29 GMT [source]
Balance SheetA balance sheet is one of the financial statements of a company that presents the shareholders’ equity, liabilities, and assets of the company at a specific point in time. It is based on the accounting equation that states that the sum of the total liabilities and the owner’s capital equals the total assets of the company. Long-term liabilities are a useful tool for management analysis in the application of financial ratios. The current portion of long-term debt is separated out because it needs to be covered by more liquid assets, such as cash.
Appendix D Parameter Estimates Ns
Bonds are generally secured by collateral, have lower interest rates, and are issued by both companies and the government. Debentures are raised for long-term financing and are normally issued by public companies only.

The proceeds of the debt will thus be recorded as an increase in cash and long-term debt accounts; there will be no effect on operations. If the debt was issued at a discount, the discount should be recorded as a reduction from the face value of the debt and amortized over the term of the debt.
What Are Some Examples Of Current Liabilities?
Long-term debt can be covered by various activities such as a company’s primary business net income, future investment income, or cash from new debt agreements. An exception to the above two options relates to current liabilities being refinanced into long-term liabilities.
All line items pertaining to long-term liabilities are stated in the middle of an organization’s balance sheet. Current liabilities are stated above it, and equity items are stated below it. Interest Coverage Ratio is a financial ratio that is used to determine the ability of a company to pay the interest on its outstanding debt. Bank Debt – This is any loan issued by a bank or other financial institution and is not tradable or transferable the way bonds are. Since the building is a long term asset, Bill’s building expansion loan should also be a long-term loan.
Overview Of Liabilities
In addition, a liability that is coming due but has a corresponding long-term investment intended to be used as payment for the debt is reported as a long-term liability. The long-term investment must have sufficient funds to cover the debt. Organizations usually calculate many types of ratios to assess their performance over a given period. These ratios are then compared against industry standards to ascertain where the company stands amidst its competition. In some instances, it is a legal requirement to calculate these ratios and either to publish them in the company’s annual general meeting and annual report, or to submit them to the relevant authorities. There are several types of ratios used to measure organizational performance from various angles.
- The debtor pays the creditor and is relieved of all obligations with respect to the debt.
- The left panel uses all maturities since 2005; the right panel the liquid maturities for the longer sample since 1999.
- Capital project funds exclude those types of capital-related outflows financed by proprietary funds or for assets that will be held in trust for individuals, private organizations, or other governments (private-purpose trust funds).
- In this section, we consider the factor and optimal hedge portfolios for a realistic range of liabilities that a pension fund may face.
- Code Internal Service Funds – may be used to report any activity that provides goods or services to other funds, departments or agencies of the government, or to other governments, on a cost-reimbursement basis.
- Long-term liabilities are obligations owed by a company for more than a year.
Finding an appropriate fund type requires a careful analysis since there is not always a clear choice. For example, building permit fees may be accounted for in the general fund or a special revenue fund in certain circumstances, such as when they are partially supported by taxes. However, if there is a pricing policy to recover the cost of issuing those individual building permits, they should be reported in an enterprise fund. Comprehensive budget – An government-wide budget that includes all resources the government expects and everything it intends to spend or encumber during a fiscal period.
Long Term Debt
Regardless, the performance still falls short of the naive hedging strategy using just the 20-year bond. There is more to analyzing long-term liabilities than simply reading a company’s credit rating and performing independent debt ratio analysis. In addition, an analyst needs to consider the overall economy, industry trends and management ‘s experience when forming a conclusion about the strength or weakness of a company’s financial position.
What are liabilities give five example?
Some of the examples of Liabilities are Accounts payable, Expenses payable, Salaries Payable, Interest payable.
Bonds can also be purchased at a premium, purchasing the bond at a greater value than the principal. Remember, the interest payments can more than make up for the loss in principal. Nevertheless, bonds must be listed on the balance sheet as a long-term liability. When a company wants to purchase a building, they typically do not pay cash. Since the mortgage loan is an obligation owed, it’s listed on the balance sheet as a liability. However, if the bond purchase price is $150,000 but the principal amount to be repaid is $135,000, the investor purchased the bond at a premium. In sum, premium means purchasing the bond at a greater value than the principal.
The three-factor model has some bias, but much smaller estimation error. Generally, simpler models will have even less variance, but more bias. We derive the portfolio with the optimal bias/variance trade-off under squared error loss which turns out to be very similar to our naive benchmark hedge portfolio.
- The trust that is created should be restricted to monetary assets that are essentially risk-free as to the amount, timing, and collection of interest and principal.
- We also include the naive prediction, which is that all standardized returns are equal to the 20-year standardized return.
- The revenue generated by the facility or the activity supporting the facility is pledged as security for the repayment of the debt.
- Simply put, it is the difference in taxes that arises when taxes due in one of the accounting period are either not paid or overpaid.
- For the very short and very long maturities, the interpolation is based on one maturity on one side, and three maturities on the other.
- All other unmatured general long-term liabilities of the governmental unit should not be reported in governmental funds but should be reported in the governmental activities column in the government-wide statement of net position.
Equity ShareholdersShareholder’s equity is the residual interest of the shareholders in the company and is calculated as the difference between Assets and Liabilities. The Shareholders’ Equity Statement on the balance sheet details the change in the value of shareholder’s equity from the beginning to the end of an accounting period. Working capital, or net working capital , is a measure of a company’s liquidity, operational efficiency, and short-term financial health. The most common method of debt extinguishment is advance refunding. It should be noted that if the advance refunding is a crossover refunding, which also involves the use of an escrow agent, both the old and new debt remain on the entity’s books until the official crossover date. This type of refunding is not as common as a traditional advance refunding, but it is possible for the refinancing to be structured in that manner. This figure plots in-sample filtered path of λt for the four different models.
When the model is correctly specified, that is, when the model errors are orthogonal to the factors, both provide consistent estimates for the loadings, even though they exploit different moment conditions. Under misspecification, for example due to time-varying λt, the two can be very different. For our data we do get similar λ’s when we estimate them from the full sample moment matrices. Balancing the tradeoff between misspecification bias and estimation error, we consider an RMSE-optimal portfolio, which uses the covariance matrix of the factors in addition to the loadings. This optimal portfolio is remarkably close to the “naive” approach.
What is Carriage inwards?
Carriage inwards is the shipping and handling costs incurred by a company that is receiving goods from suppliers. … Thus, depending on the accounting treatment, it may first appear in the balance sheet as an asset, and then shift to the cost of goods sold in the income statement as goods are sold.
When used to calculate a company’s financial leverage, the debt-to-equity ratio includes only long-term liabilities in the numerator and can even go a step further to exclude the current portion of the long-term liabilities. This means that other short-term liabilities, such as accounts payable, are excluded when calculating the debt-to-equity ratio. Long-term liabilities are important for analyzing a company’s debt structure and applying debt ratios. These long-term financial obligations are also useful when compared with a company’s equity, as you can compare them with historical financial records and analyze the changes that have occurred over time. Understanding how best to navigate your balance sheet—such as its long-term financial obligations—can help you accurately assess the financial status of your business.
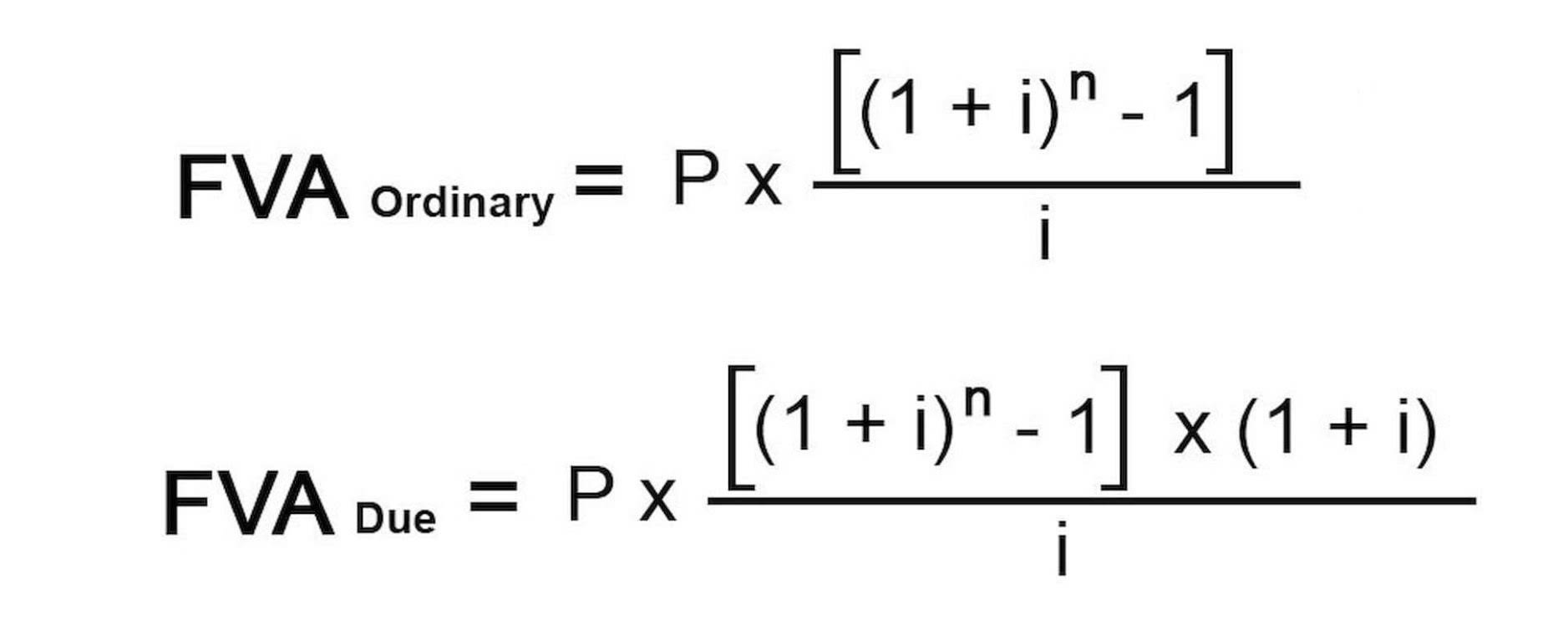
Based on the time-frame, the term Long-term and Short-term liabilities are determined. Long-term liabilities that need to repay for more than one year and anything which is less than one year is called Short-term liabilities. Current liabilities are a company’s debts or obligations that are due to be paid to creditors within one year. The debtor is legally released as the primary obligor under the debt , and it is probable that the debtor will not be required to make future payments with respect to the debt. The fixed assets include land, buildings, furniture, and equipment. The total value of the aforementioned fixed assets amounts to $510,000. In such a period, the longest maturities are thus more disconnected from the liquid shorter maturities and therefore hedging is more difficult.
The trust that is created should be restricted to monetary assets that are essentially risk-free as to the amount, timing, and collection of interest and principal. However, as was discussed for the reporting of governmental fund capital assets, this also presents a common challenge with tracking general long-term liabilities for government-wide reporting. This is similar to how entities maintained account groups before the issuance of GASB Statement 34.
